SAMLKeysAndCertificates
A Primer on SAML Keys and Certificates
Contents
Terminology
KeyDescriptor of type “signing”: A
<md:KeyDescriptor use=”signing”>element in SAML metadataKeyDescriptor of type “encryption”: A
<md:KeyDescriptor use=”encryption”>element in SAML metadataSigning certificate: A public key certificate bound to a KeyDescriptor of type “signing” in SAML metadata. A signing certificate is indistinguishable from a back-channel TLS certificate in metadata.
Back-channel TLS certificate: A public key certificate bound to a KeyDescriptor of type “signing” in SAML metadata. A back-channel TLS certificate is indistinguishable from a signing certificate in metadata.
Encryption certificate: A public key certificate bound to a KeyDescriptor of type “encryption” in SAML metadata.
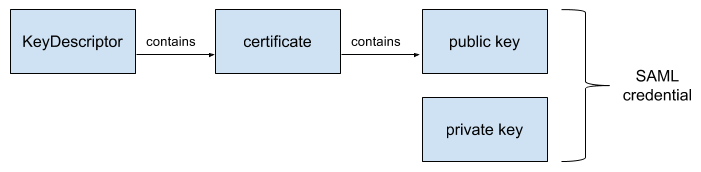
Credential: A private key plus its corresponding public key certificate.
Signing credential: A key pair used for XML Signature. The public key is bound to a signing certificate in metadata. The private key is securely held by the party that signs the XML message.
Back-channel TLS credential: A key pair used for back-channel TLS authentication. The public key is bound to a back-channel TLS certificate in metadata. The private key is securely held by the party to be authenticated.
Encryption credential: A key pair used for XML Encryption. The public key is bound to an encryption certificate in metadata. The private key is securely held by the party that decrypts the XML message.
The KeyDescriptor Element
There are two types of KeyDescriptors in SAML metadata: the signing KeyDescriptor type and the encryption KeyDescriptor type. These KeyDescriptor types correspond to the following metadata elements (resp.):
<md:KeyDescriptor use=”signing”><md:KeyDescriptor use=”encryption”>
In other words, a KeyDescriptor type is a particular type of <md:KeyDescriptor> element in SAML metadata.
Signing KeyDescriptor Type
The signing KeyDescriptor type corresponds to an <md:KeyDescriptor use=”signing”> element in metadata. The actual certificate contained by this metadata element enables message-level signing (i.e., XML Signature) or back-channel TLS authentication (or both).
Encryption KeyDescriptor Type
The encryption KeyDescriptor type corresponds an <md:KeyDescriptor use=”encryption”> element in metadata. The actual certificate contained by this metadata element enables message-level encryption (i.e., XML Encryption).
The use XML attribute
According to the SAML metadata schema, the md:KeyDescriptor/@use XML attribute is an optional attribute. A KeyDescriptor with no use XML attribute such as
<md:KeyDescriptor>
is merely an optimization for a pair of contiguous elements
<md:KeyDescriptor use=”signing”><md:KeyDescriptor use=”encryption”>
each with exactly the same content.
KeyDescriptor Content
In practice, the content of any given <md:KeyDescriptor> element is a public key certificate. There are three types of certificates in metadata
- Signing certificate
- Back-channel TLS certificate
- Encryption certificate
A KeyDescriptor of type “signing” contains either a signing certificate or a back-channel TLS certificate while a KeyDescriptor of type “encryption” contains an encryption certificate.
A KeyDescriptor of type “signing” is ambiguous
Using a signing certificate
Using an encryption certificate
In an X.509 public key infrastructure, a certificate binds a public key to a subject name. In a SAML public key infrastructure, a certificate is merely a convenient wrapper for a public key.
SAML Keys and Certificates
Signing Key and Certificate
A signing credential is a key pair used for XML Signature, which provides authenticity and integrity at the message level. The public key is bound to a signing certificate in metadata. The private key is securely held by the party that signs the XML message.
TLS Key and Certificate
A TLS credential is a key pair used for back-channel TLS authentication, which provides authenticity, integrity, and confidentiality at the transport level. The public key is bound to a back-channel TLS certificate in metadata. The private key is securely held by the party to be authenticated.
Encryption Key and Certificate
By definition, an encryption credential is a key pair used for XML Encryption, which provides authenticity and confidentiality at the message level. The public key is bound to the encryption certificate in metadata. The private key is securely held by the party that decrypts the XML message.
Example
Creating a SAML Key and Certificate
This section shows how to use the openssl command-line tool to create a key pair with a long-lived, self-signed certificate.
Security Alert!
-nodes option to enable encryption of the private key. When the -nodes option is removed, the tool will prompt the user for a decryption password.# change these values as needed $ OUT_DIR=/tmp/credentials $ LIFETIME=3650 # 10 yrs # normally, only a back-channel TLS certificate needs a subject name # but it doesn't hurt to add this to a signing or encryption certificate $ SUBJECT_NAME='/CN=hostname.example.org' # create a 2048-bit key with long-lived, self-signed certificate $ /usr/bin/openssl req -new -x509 -nodes \ -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout $OUT_DIR/key.pem \ -days $LIFETIME -subj $SUBJECT_NAME -out $OUT_DIR/cert.pem
Inspecting the SAML Certificate
Use the openssl command-line tool to inspect the certificate created in the previous section. Note that the certificate contains a 2048-bit public key.
# inspect the certificate
$ /usr/bin/openssl x509 -text -in $OUT_DIR/cert.pem
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number:
92:bf:75:98:a6:ed:22:4c
Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
Issuer: CN=hostname.example.org
Validity
Not Before: Jun 4 22:42:33 2016 GMT
Not After : Jun 2 22:42:33 2026 GMT
Subject: CN=hostname.example.org
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption
RSA Public Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus (2048 bit):
00:dd:a9:e8:c0:8a:de:66:29:b1:bf:f1:ff:ae:6f:
20:24:61:4e:e4:63:77:23:58:8d:6a:5f:7f:8b:d6:
56:b4:1a:3e:cb:61:cc:cc:a6:f4:91:64:5c:d8:f5:
cc:f7:68:74:b1:24:5e:c7:ac:1e:18:12:83:26:01:
f7:cf:ca:b2:a4:da:ee:d8:3e:cf:03:b9:de:ba:84:
9c:c8:e1:02:cf:5c:41:ac:83:e5:e2:40:8e:dc:80:
e6:6c:19:44:ee:9c:62:80:f9:30:f7:25:b8:76:d1:
b5:c0:fb:41:63:6f:09:c3:20:21:5f:f5:9a:e9:53:
86:e7:f1:4d:bc:dd:6f:ac:2c:69:6d:f4:34:3a:8e:
52:05:93:70:60:c8:37:52:5f:90:e6:47:ad:fd:ef:
b2:42:a2:94:a0:bc:c1:65:f4:c3:01:17:0e:03:4e:
1a:d2:7b:02:47:ad:08:ca:54:06:93:c7:ed:d2:01:
bd:00:ca:7d:8e:bb:bd:5f:6d:b8:67:39:40:a6:bb:
3d:5a:79:37:a2:4a:49:c1:ec:41:2e:51:c5:39:e3:
d4:4c:50:56:f2:97:77:3e:ed:68:77:87:2f:c0:aa:
bd:5f:62:e4:b3:c8:63:e8:e7:b5:9d:1b:bc:ae:da:
a9:7e:36:de:33:f2:ae:8f:04:07:de:e8:d9:65:20:
d7:45
Exponent: 65537 (0x10001)
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
36:DF:9D:01:14:C7:25:E1:6F:BE:F7:A9:BF:92:93:DA:17:76:3E:1E
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:36:DF:9D:01:14:C7:25:E1:6F:BE:F7:A9:BF:92:93:DA:17:76:3E:1E
DirName:/CN=hostname.example.org
serial:92:BF:75:98:A6:ED:22:4C
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA:TRUE
Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
85:d1:34:67:46:9c:b8:32:15:e0:bb:78:fb:23:53:59:8b:7b:
9d:71:a0:df:62:17:5f:67:97:f0:51:76:a5:79:5c:c3:56:83:
51:bf:8a:f6:1a:74:86:4b:31:fd:a2:f4:ea:f9:54:57:5d:ea:
f7:9e:a9:ee:c4:79:0e:33:d7:eb:d9:66:7e:12:13:87:c1:82:
ab:81:c6:24:97:8e:a1:74:c7:2e:1d:70:4e:63:d6:d7:0c:44:
65:a2:bd:46:aa:35:a8:dc:e3:51:a3:84:50:d0:50:ae:b0:8e:
7e:32:15:8c:88:68:35:59:0a:b8:09:e6:60:f5:02:f7:50:ea:
57:8d:3d:45:8d:c3:c1:8c:54:27:4b:b8:c0:58:b6:2d:a8:c8:
bc:6c:ce:6c:ab:77:1a:b5:dc:e6:5d:ac:d6:e5:1f:b5:6d:17:
9c:70:45:e7:2f:86:3d:72:aa:78:5d:ab:bd:f9:79:f3:dd:6f:
15:0b:16:18:c4:6b:81:04:62:13:76:36:af:b9:02:84:d1:39:
76:3b:bd:3a:4a:33:f9:97:43:dc:ae:52:71:b7:e7:c1:02:a0:
c2:03:4f:ff:1e:d6:12:25:57:df:58:79:94:1e:c3:08:c3:b6:
fe:b9:69:43:14:6f:4e:1c:a8:8c:ed:41:dc:fc:b2:4e:75:3a:
20:67:51:9d
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDQjCCAiqgAwIBAgIJAJK/dZim7SJMMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMB8xHTAbBgNV
BAMTFGhvc3RuYW1lLmV4YW1wbGUub3JnMB4XDTE2MDYwNDIyNDIzM1oXDTI2MDYw
MjIyNDIzM1owHzEdMBsGA1UEAxMUaG9zdG5hbWUuZXhhbXBsZS5vcmcwggEiMA0G
CSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4IBDwAwggEKAoIBAQDdqejAit5mKbG/8f+ubyAkYU7kY3cj
WI1qX3+L1la0Gj7LYczMpvSRZFzY9cz3aHSxJF7HrB4YEoMmAffPyrKk2u7YPs8D
ud66hJzI4QLPXEGsg+XiQI7cgOZsGUTunGKA+TD3Jbh20bXA+0FjbwnDICFf9Zrp
U4bn8U283W+sLGlt9DQ6jlIFk3BgyDdSX5DmR63977JCopSgvMFl9MMBFw4DThrS
ewJHrQjKVAaTx+3SAb0Ayn2Ou71fbbhnOUCmuz1aeTeiSknB7EEuUcU549RMUFby
l3c+7Wh3hy/Aqr1fYuSzyGPo57WdG7yu2ql+Nt4z8q6PBAfe6NllINdFAgMBAAGj
gYAwfjAdBgNVHQ4EFgQUNt+dARTHJeFvvvepv5KT2hd2Ph4wTwYDVR0jBEgwRoAU
Nt+dARTHJeFvvvepv5KT2hd2Ph6hI6QhMB8xHTAbBgNVBAMTFGhvc3RuYW1lLmV4
YW1wbGUub3JnggkAkr91mKbtIkwwDAYDVR0TBAUwAwEB/zANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUF
AAOCAQEAhdE0Z0acuDIV4Lt4+yNTWYt7nXGg32IXX2eX8FF2pXlcw1aDUb+K9hp0
hksx/aL06vlUV13q956p7sR5DjPX69lmfhITh8GCq4HGJJeOoXTHLh1wTmPW1wxE
ZaK9Rqo1qNzjUaOEUNBQrrCOfjIVjIhoNVkKuAnmYPUC91DqV409RY3DwYxUJ0u4
wFi2LajIvGzObKt3GrXc5l2s1uUftW0XnHBF5y+GPXKqeF2rvfl5891vFQsWGMRr
gQRiE3Y2r7kChNE5dju9Okoz+ZdD3K5ScbfnwQKgwgNP/x7WEiVX31h5lB7DCMO2
/rlpQxRvThyojO1B3PyyTnU6IGdRnQ==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
Note the PEM-encoded certificate appended to the output. In the next section, we will insert that certificate into SAML metadata.
Binding the SAML Certificate to a KeyDescriptor in Metadata
Finally, bind the above certificate to an <md:KeyDescriptor use="signing"> element in SAML metadata:
<md:KeyDescriptor use=”signing”>
<ds:KeyInfo>
<ds:X509Data>
<ds:X509Certificate>
MIIDQjCCAiqgAwIBAgIJAJK/dZim7SJMMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBBQUAMB8xHTAbBgNV
BAMTFGhvc3RuYW1lLmV4YW1wbGUub3JnMB4XDTE2MDYwNDIyNDIzM1oXDTI2MDYw
MjIyNDIzM1owHzEdMBsGA1UEAxMUaG9zdG5hbWUuZXhhbXBsZS5vcmcwggEiMA0G
CSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4IBDwAwggEKAoIBAQDdqejAit5mKbG/8f+ubyAkYU7kY3cj
WI1qX3+L1la0Gj7LYczMpvSRZFzY9cz3aHSxJF7HrB4YEoMmAffPyrKk2u7YPs8D
ud66hJzI4QLPXEGsg+XiQI7cgOZsGUTunGKA+TD3Jbh20bXA+0FjbwnDICFf9Zrp
U4bn8U283W+sLGlt9DQ6jlIFk3BgyDdSX5DmR63977JCopSgvMFl9MMBFw4DThrS
ewJHrQjKVAaTx+3SAb0Ayn2Ou71fbbhnOUCmuz1aeTeiSknB7EEuUcU549RMUFby
l3c+7Wh3hy/Aqr1fYuSzyGPo57WdG7yu2ql+Nt4z8q6PBAfe6NllINdFAgMBAAGj
gYAwfjAdBgNVHQ4EFgQUNt+dARTHJeFvvvepv5KT2hd2Ph4wTwYDVR0jBEgwRoAU
Nt+dARTHJeFvvvepv5KT2hd2Ph6hI6QhMB8xHTAbBgNVBAMTFGhvc3RuYW1lLmV4
YW1wbGUub3JnggkAkr91mKbtIkwwDAYDVR0TBAUwAwEB/zANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUF
AAOCAQEAhdE0Z0acuDIV4Lt4+yNTWYt7nXGg32IXX2eX8FF2pXlcw1aDUb+K9hp0
hksx/aL06vlUV13q956p7sR5DjPX69lmfhITh8GCq4HGJJeOoXTHLh1wTmPW1wxE
ZaK9Rqo1qNzjUaOEUNBQrrCOfjIVjIhoNVkKuAnmYPUC91DqV409RY3DwYxUJ0u4
wFi2LajIvGzObKt3GrXc5l2s1uUftW0XnHBF5y+GPXKqeF2rvfl5891vFQsWGMRr
gQRiE3Y2r7kChNE5dju9Okoz+ZdD3K5ScbfnwQKgwgNP/x7WEiVX31h5lB7DCMO2
/rlpQxRvThyojO1B3PyyTnU6IGdRnQ==
</ds:X509Certificate>
</ds:X509Data>
</ds:KeyInfo>
</md:KeyDescriptor>
The above certificate is either a signing certificate or a back-channel TLS certificate (or both).